What Is Heel Pain And How You Can Overcome It
Overview
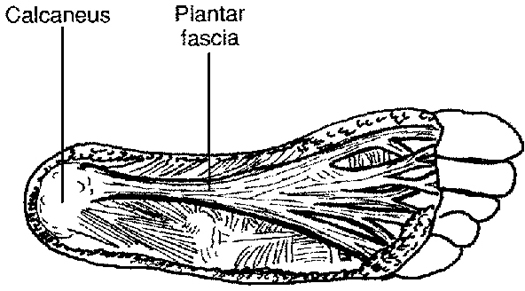
At the bottom of your foot there's a thick band of connective tissue called the plantar fascia or arch tendon. It connects your heel bone (calcaneus) to the front of your foot. If the plantar fascia becomes irritated and sore from overuse, it's known as plantar fasciitis. Plantar fasciitis sometimes can be mistaken for heel spurs, which is a different kind of injury with similar symptoms. Plantar fasciitis is a common cause of heel pain in runners, dancers, and athletes in sports that involve a lot of running or jumping. You don't have to be active to get plantar fasciitis. It can affect anyone. People who are overweight, pregnant women, people whose jobs involve a lot of standing, and people who wear worn-out shoes all have a higher chance of getting plantar fasciitis.
Causes
There are multiple potential causes and contributing factors to plantar fasciitis heel pain. The structure of a personâs foot and the way that they walk or run usually play a significant role in the development of plantar fasciitis. Those with an arch that is lower or higher than the average person are more likely to be afflicted. Overexertion and/or participating in activities that a person is not accustomed to also place a person at risk. This can include a heavy workout, a job change, or even an extended shopping trip. Additionally, inappropriate shoes are also often a factor. Exercising in shoes that are worn out or donât have enough support and/or wearing inexpensive, flimsy or flat-soled dress or casual shoes are common culprits. In warm climates, such as here in Southern California, people who wear flip-flop sandals or even go barefoot throughout the year increase their chances of developing heel pain. Many athletes and weekend warriors develop heel or arch pain from over-exertion during running or other sports. People who work at jobs that involve long periods of standing, such as grocery checkers, cashiers, warehouse workers, postal workers, and teachers are more susceptible as well. Adults of all ages can develop plantar fasciitis. Heel pain in children is usually caused by a different type of condition.
Symptoms
The heel pain characteristic of plantar fasciitis is usually felt on the bottom of the heel and is most intense with the first steps of the day. Individuals with plantar fasciitis often have difficulty with dorsiflexion of the foot, an action in which the foot is brought toward the shin. This difficulty is usually due to tightness of the calf muscle or Achilles tendon, the latter of which is connected to the back of the plantar fascia. Most cases of plantar fasciitis resolve on their own with time and respond well to conservative methods of treatment.
Diagnosis
Physical examination is the best way to determine if you have plantar fasciitis. Your doctor examines the affected area to determine if plantar fasciitis is the cause of your pain. The doctor may also examine you while you are sitting, standing, and walking. It is important to discuss your daily routine with your doctor. An occupation in which you stand for long periods of time may cause plantar fasciitis. An X-ray may reveal a heel spur. The actual heel spur is not painful. The presence of a heel spur suggests that the plantar fascia has been pulled and stretched excessively for a long period of time, sometimes months or years. If you have plantar fasciitis, you may or may not have a heel spur. Even if your plantar fasciitis becomes less bothersome, the heel spur will remain.
Non Surgical Treatment
Many types of treatment have been used to combat plantar fasciitis, including injections, anti-inflammatory medications, orthotics, taping, manipulation, night splinting, and instrument-assisted soft-tissue manipulation (IASTM). IASTM begins with heat, followed by stretching. Stretching may be enhanced by applying ice to the plantar fascia. These stretches should be performed several times per day, with the calf in the stretched position. IASTM uses stainless-steel instruments to effectively access small areas of the foot. IASTM is believed to cause a secondary trauma to injured soft tissues as part of the healing process. Therapeutic modalities such as low-level laser, ultrasound, and electrical muscular stimulation may be effective in the reduction of pain and inflammation. Low Dye strapping or taping of the foot is an essential part of successful treatment of plantar fasciitis. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy (ESWT) was introduced with great promise at one time. Recent studies have reported less favorable results. Some report no effect. Previous local steroid injection may actually have a negative effect on results from ESWT.

Surgical Treatment
When more conservative methods have failed to reduce plantar fasciitis pain, your doctor may suggest extracorporeal shock wave therapy, which is used to treat chronic plantar fasciitis. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy uses sound waves to stimulate healing, but may cause bruises, numbness, tingling, swelling, and pain. When all else fails, surgery may be recommended to detach the plantar fascia from the heel bone. Few people need surgery to treat the condition.
Prevention
Plantar fasciitis can be a nagging problem, which gets worse and more difficult to treat the longer it's present. To prevent plantar fasciitis, run on soft surfaces, keep mileage increases to less than 10 percent per week, and visit a specialty running shop to make sure you're wearing the proper shoes for your foot type and gait. It's also important to stretch the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon.
